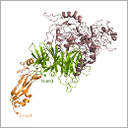
Mycoplasma genitalium is a sexually transmitted bacterium responsible for several genitourinary disorders. An estimated 1% of the adult population is infected with this bacterium. Using XALOC beamline at the ALBA Synchrotron it has been defined the structure of the protein involved in the pathogen’s adhesion process. The discovery opens the door to defining new therapeutic strategies to fight this pathogen which is becoming more and more resistant to antibiotics.
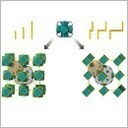
The Science magazine highlighted in the section “Research in other journals” the article recently published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) by researchers from the ICN2 Supramolecular Nanochemistry and Materials Group. The article reports about zigzag linkers for transversal design in reticular chemistry. During the experiments, measurements were performed in the ALBA Synchrotron, at the XALOC beamline.
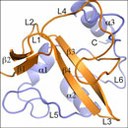
Using synchrotron light, researchers from CIC bioGUNE have solved the structure of RavN, a protein that Legionella pneumophila uses for stealing functions and resources of the host cell.
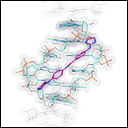
A team led by researchers from the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) has unveiled the mechanism of action of two drugs, FR60 and JNI18, which cure 100% of mice with sleeping sickness, also called African trypanosomiasis. Using synchrotron light at the ALBA Synchrotron, they have observed how these drugs perfectly stacked on the Trypanosoma brucei’s DNA, the parasite that causes the disease. Blocking and inflicting specific damage on its DNA, the parasite cannot reproduce and finally dies after 4-5 days. Scientists conclude drugs are effective potential treatments against sleeping sickness, which threats over 55 million people in sub-Saharan Africa countries. These drugs remain patent-free to gain interest among pharmaceutical labs.
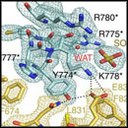
An international research lead by Institute of Biomedicine of the University of Barcelona (IBUB) and the Research Institute of the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau (IIB Sant Pau) shows, for the first time, the three-dimensional structure of the homodimeric androgen receptor ligand-binding domain. In order to solve the 3D structure of the protein, X-ray diffraction analyses have been conducted at the XALOC beamline of the ALBA Synchrotron.




