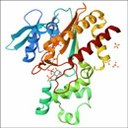
X-rays produced at the ALBA Synchrotron have enabled to determine 1,000 protein structures in a decade. Number 1,000 is part of a study led by CSIC scientists that can contribute to design new therapies. XALOC beamline at ALBA, devoted to macromolecular crystallography, has made possible this achievement.
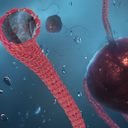
A multidisciplinary research team lead by researchers from CIC bioGUNE has revealed the structure of one of the cellular machineries for protein recycling. This machinery is responsible for transporting and reusing over 60 different proteins. Experiments carried out at the XALOC beamline of the ALBA Synchrotron enabled the understanding of the protein recycling process at an atomic level.
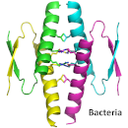
ALBA researchers from the XALOC beamline have discovered a common transcription factor protein domain in bacteria and humans. They named it TetD. This discovery shows that the basic functional principles of the system are very similar for living beings and suggests the existence of a common ancestor before multicellular life appeared. Moreover, the human protein that presents TetD is related with the occurrence of cancer, thus this study can help in the understanding of the regulation of cancer development.
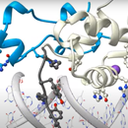
Researchers at IRB Barcelona managed to carry out a structural analysis of the FoxH1 protein in unprecedented detail. The study, with data obtained at the XALOC beamline of the ALBA Synchrotron, has revealed how this protein binds to different DNA sites in embryonic development and in tumors associated with high levels of gene expression. That shows its underlying potential for developing treatments against diseases related with this process.
Human aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3 (ALDH1A3) is an enzyme that binds ATP, as well as a biomarker of tumor-initiating cells responsible for resistance to chemotherapy. According to a study by the UAB Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology in collaboration with the ALBA Synchrotron, their silencing restores the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents.




