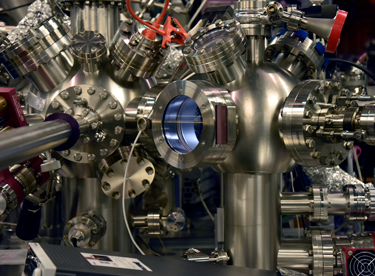
Researchers propose and demonstrate for the first time a new concept for the transfer of magnetic data in three dimensions based on geometrical effects for the interconnection of functional spintronic planes. The device is based on a magnetic nanostructure and promotes the spontaneous motion of bits without the need to apply any external stimuli. This work has promising applications in spintronics. Experiments at the CIRCE beamline in ALBA were key to characterize the magnetic structures and confirm their functioning.
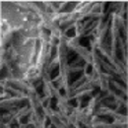
Researchers from the UCM and CSIC, in collaboration with ALBA, have established a novel synthesis protocol to produce a larger number of nanowires than conventional laboratory fabrication processes with considerably reduced production time and cost. The use of recycled aluminium and the fact that the nanowires growth process is performed at room temperature allows the nanowires to be used in industry at lower costs. CIRCE beamline from ALBA has contributed to the evaluation of the magnetic properties of the nanowires for application in permanent magnets.

Researchers from the IMDEA Energy Institute in Madrid have used the CIRCE-NAPP beamline of ALBA to study the artificial photosynthesis process, that is, the chemical reaction that plants and other photosynthetic organisms use to transform the Sun's energy into chemical energy. The goal of their research is to selectively control the products of the chemical reaction to obtain those that have industrial and energetic interest. At the CIRCE-NAPP station, scientists have analyzed the different reaction products based on the catalysts used.
An international collaboration, led by the Autonomous University of Madrid, has studied the electrical properties of a few layers thick sheets of antimonen, a two-dimensional material composed of antimony atoms. The results indicate an electrical transport that occurs mainly on the surface of the material. This, coupled with its stability and simple structure, make it a promising candidate for nanoelectronic and optoelectronic applications. Part of the experiments were carried out at the CIRCE beamline.
They proved that a system based on molybdenum-on-titania does efficiently catalyze this reaction and represents a promising alternative to current industrial catalysts. This helps eliminating carbon dioxide and producing methanol, which can serve as a "green fuel" or as building blocks for the production of plastics, pharmaceuticals, textiles, etc. The team carried out experiments at the CIRCE-NAPP beamline of the ALBA Synchrotron to characterize the structure of the catalyst.